Unlocking the Secrets of DSIP Peptides
Share
Origins & Discovery
DSIP stands for Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide, first identified in the mid-1970s when researchers isolated it from the brains of rabbits during slow-wave (delta) sleep WikipediaSwolverine.
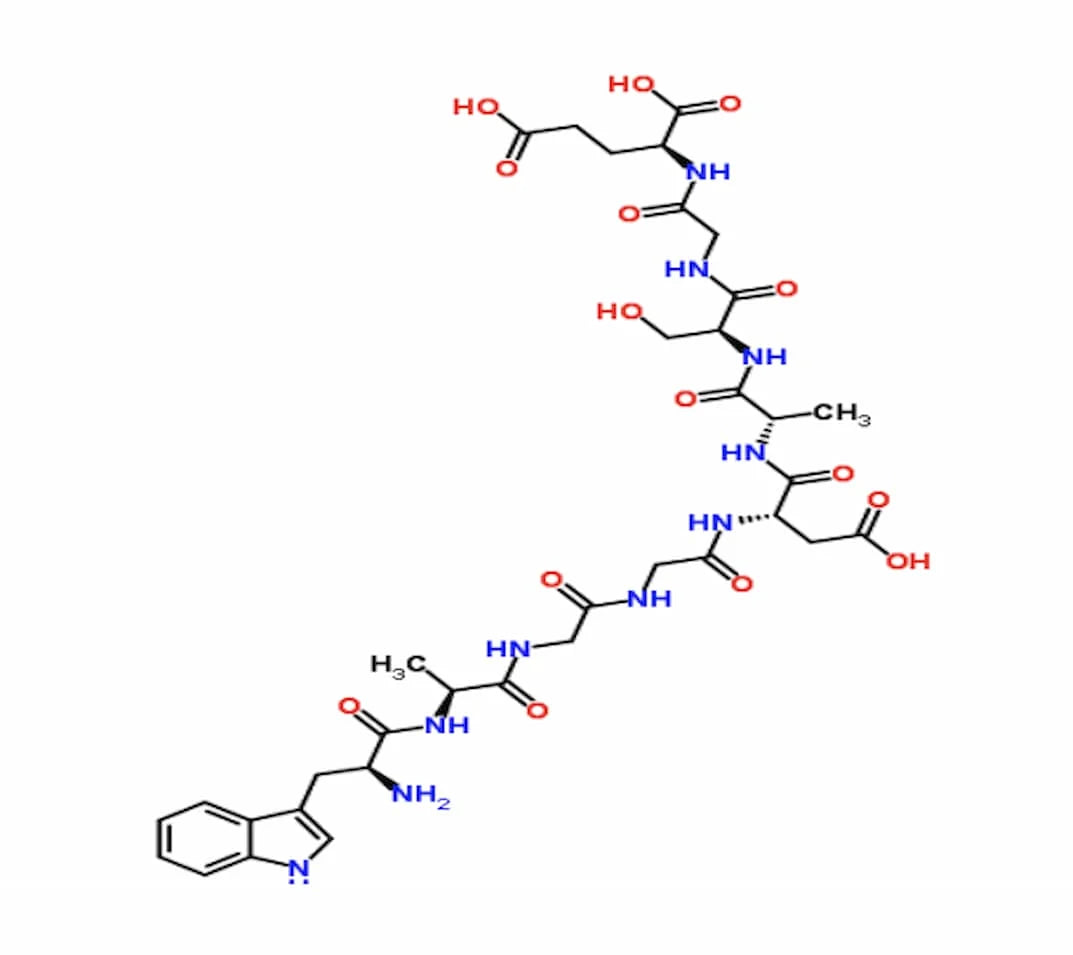
It’s a nonapeptide, meaning it’s composed of just nine amino acids (Trp-Ala-Gly-Gly-Asp-Ala-Ser-Gly-Glu) WikipediaPeptide Sciences.
Despite being named for inducing sleep, DSIP’s full biological origin isn't confirmed; interestingly, genetic searches suggest it might trace back to bacterial sources Wikipedia.
How DSIP Might Work
Though not fully understood, DSIP appears to influence several key systems in the body:
Sleep Regulation: It promotes deep (delta) sleep and has been tied to improvements in sleep efficiency and latency—particularly in insomnia cases SwolverinePeptide SciencesInnerbodyPubMedWellness At Century City.
Neuroendocrine Modulation: DSIP interacts with GABAergic, NMDA, and adrenergic pathways, and influences hormones such as cortisol, LH, and growth hormone SwolverinePeptide SciencesPeptidesWikipedia.
Stress & Antioxidant Effects: It appears to reduce stress responses, enhance oxidative phosphorylation, and offer some antioxidant and stress-protective benefits Peptide Sciences+1Innerbody.
Pain and Recovery: DSIP shows potential in reducing chronic pain, aiding opioid withdrawal, and improving mood via interaction with opioid receptors—without causing dependence Peptide SciencesInnerbodyPeptides.
A Glimpse at the Research Landscape
| Area | Summary |
|---|---|
| Sleep | Animal and limited human trials show enhanced sleep depth and efficiency, but results vary in strength PubMedInnerbodyPeptide Sciences. |
| Stress & Mood | DSIP may improve stress tolerance and induce relaxation; these effects could stem from better sleep or direct brain modulation InnerbodyPeptide Sciences. |
| Withdrawal & Pain | Promising findings suggest DSIP reduces symptoms during alcohol and opioid withdrawal and lowers pain levels in migraine and psychogenic pain cases Innerbody+1Peptides. |
| Physiological Functions | Research hints at roles in blood pressure regulation, thermogenesis, antioxidant defense, and even tumor prevention in animal models WikipediaPeptide SciencesInnerbody. |
Practical Insights: Use, Dosage & Legal Status
Not an Approved Treatment: DSIP is considered a research-only compound and lacks FDA approval SwolverineRevolution Health & WellnessPeptide Sciences.
Typical Administration: In research contexts, it’s often supplied as a lyophilized powder, reconstituted with sterile water, and administered via injection (commonly subcutaneous). Human dosing in literature ranges from 0.1 mg to 0.5 mg daily Revolution Health & WellnessPeptide SciencesPeptides.
Safety & Limitations: Studies involve very small sample sizes. While effects on sleep and mood are reported, they are often modest or inconsistent, and long-term safety isn’t well-established PubMedInnerbodySwolverine.
Summary Snapshot
DSIP is a compelling neuromodulator—with a name that reflects its sleep-related origins—that may gently enhance deep sleep, modulate hormones, relieve stress, help with pain, and support recovery. However, it remains experimental, with research highlighting both promise and uncertainties.
Final Thoughts
Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide (DSIP) represents a fascinating frontier in sleep and recovery science. It shows potential beyond sedative effects—possibly restoring natural sleep architecture and enhancing resilience. Yet, until larger, well-controlled studies are conducted, it’s best viewed as a research molecule, not a clinical solution.

